Heat Transfer Oil or Heat Transfer Oil

Heat transfer is a thermal engineering discipline that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of heat and heat energy between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and energy transfer through phase changes. Engineers also consider the mass transfer of different chemical species, whether cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have different characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system.
- Non-flammable and volatile. This means that the lubricant must have a high flash point.
- Not easily damaged carbon chains / lubrication bonding elements. The broken carbon chain can be seen from the change in color from its original color to dark (oxidized). This means that the base material of the lubricant must come from the processing of petroleum containing long carbon chains
- Easily absorbs heat and provides heat and has stable properties (temperature range is not large). Because heating is more evenly distributed, the risk of fire can be reduced, which may occur due to heat which directly hits the materials being processed.
- Easy to move /

Heat Transfer Oil Boilers move means the lubricant can carry heat from the heat source to the media to be heated by transferring the pump
- It is not corrosive and can carry impurities in the heating system.
- Please note that the circulation system is totally closed to prevent oxidation, pollution and evaporation.
- The flow rate of the lubricant must remain controlled to prevent certain places from overheating (usually between 1.5 – 3 meters per second)
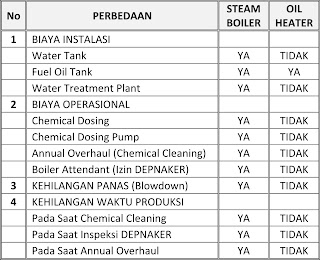
- Efficiency, many people believe that heat-conductive lubricants have an efficiency of 5 to 8% better than the use of conventional steam systems, this is because in conventional steam systems there are many heat losses such as in steam traps 6% to 14% depending on the length of the installation pipe of the system . Besides heat loss in water blowdown up to 3%, and heat loss in deaerator up to 2%.
- Certification, to operate a pressurized steam system requires certification of both the operator who runs it and the installation itself, in many countries this is a law that must be obeyed so that it impacts on operational costs.
- Unlike pressurized steam systems, almost all heat installations using heat-conducting lubricants operate at atmospheric pressure. The pressure on this system is only limited to the pressure of the circulating pump used, which only ranges from 2-4 bar.
- Corrosion, the steam system is very susceptible to corrosion, air and salt contained in water are the main components causing corrosion. Vapors are also very abrasive to metals because there is no luminance.
- The heat transfer system used to heat the lubricant is non-corrosive and has the same lubricating properties as the lubricating oil so that it does not cause corrosion and abrasion on the metal.
- Maintenance, due to the absence of steam traps, condensate returns, and chemical dosing on boiler water in heating systems that use heat-conductive lubricants, automatically the maintenance is also less.
- Environmentally friendly, more environmentally friendly compared to steam boilers whose use of water must be processed mechanically and chemically so that the disposal of waste water must be safe for the environment.
- Safety, unlike steam boilers that require high pressure for high operating temperatures, thermal fluid heaters operate at atmospheric pressure so it is very safe. The pressure that occurs in the thermal fluid heaters system is only due to the pressure of the circulating pump and not the pressure due to the pressure needed to reach the desired working temperature.
- Temperature control, Temperature control in the lubricant heating system is carried out directly at the temperature of the lubricant, so it is more accurate than the steam boiler which is regulated by regulating the working pressure of the system
- The costs, investment and operating costs of a heating system using a heat transfer lubricant are relatively lower compared to steam boilers.